Spring IoC와 DI, 그리고 DI 주입 방법
Table of contents
Spring IoC와 DI란?
IoC란 Inversion of Control의 약자이며 제어의 역전이라고도 불린다.
객체의 생성부터 생명주기 관리까지 객체에 대한 제어를 프레임워크가 해주기 때문에 사용하는 용어이다.
Spring에서는 IoC 컨테이너가 객체를 생성하고 생명주기를 관리하는 역할을 담당한다.
@Service
public class SpringService{
SpringRepository springRepository = new SpringRepository();
}
위와 같은 방식은 객체를 코드로서(개발자가) 직접 생성하고 제어했다.
@Service
public class SpringService{
SpringRepository springRepository;
@Autowired
public SpringService(SpringRepository springRepository){
this.springRepository = springRepository;
}
}
위와 같이 작성하면, 스프링은 필요한 시점에 객체를 주입해준다.
주입해주는 과정을 DI라고 하는데, 스프링이 내부에 있는 객체들간의 관계를 관리할 때 사용하는 기법이다.
장점은, 어떤 SpringRepository가 interface이고, 이 interface를 구현한 다른 객체가 bean으로 등록되어있는 경우, 스프링이 알아서 주입을 해준다는 점이다.
따라서 모듈 간의 결합도가 낮아지고 유연성이 높아진다는 장점이 있다.
스프링 컨테이너 종류
스프링 컨테이너가 관리하는 객체를 빈(Bean)이라고 한다.
Bean Factory
객체를 생성하고 DI 처리를 해준다.
Bean 등록, 생성, 조회, 반환을 관리한다.
ApplicationContext
Bean Factory와 유사하지만, 더 많은 기능을 제공한다.
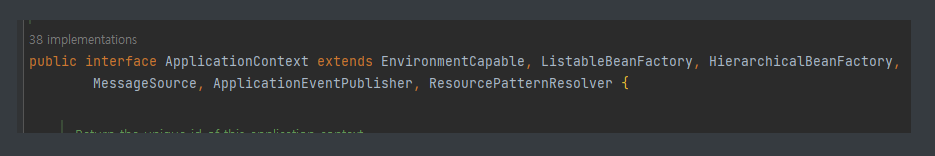
위와 같이, ApplicationContext는 BeanFactory를 포함해서 다른 인터페이스도 상속하고 있다.
BeanFactory의 모든 기능을 상속받으며 다른 부가 기능을 제공하기 때문에 BeanFactory보다는 보통 ApplicationContext를 사용한다.
DI 방법과 특징
필드 주입(@Autowired) 방식
@Service
public class SpringService{
@Autowired
SpringRepository springRepository;
}
위 방식은 생성자 주입 방식에 비해 의존 관계를 한 눈에 파악하기 어렵다는 단점이 있고
final 선언을 할 수 없어 불변성을 보장할 수 없으며 순환 참조가 발생할 수 있다.
수정자(setter) 주입 방식
@Service
public class SpringService{
private SpringRepository springRepository;
@Autowired
public void setSpringRepository(SpringRepository springRepository) {
this.springRepository = springRepository;
}
}
위 방식은 구현체(SpringRepository)를 주입하지 않아도 SpringService를 생성해서 사용할 수 있어서 구현체와 관련있는 메서드를 사용하게 되었을 때 NPE가 발생할 수 있다.
또한, 순환 참조 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
생성자 주입 방식
@Service
public class SpringService {
private final SpringRepository springRepository;
@Autowired
public SpringService(SpringRepository springRepository) {
this.springRepository = springRepository;
}
}
의존 관계를 모두 주입해야 객체 생성이 가능해서 NPE 발생을 방지할 수 있다.
final 키워드를 통해 불변성을 보장할 수 있고
스프링 컨테이너가 빈을 생성할 때 생성자 주입 방식은 순환참조를 확인하기 때문에 순환 참조를 컴파일 단계에서 찾아낼 수 있다.