Spring Boot MySQL Master-Slave 기능 구현하기
Table of contents
데이터베이스 분산의 장점
- 고가용성 : 애플리케이션 등이 항상 사용 가능한 상태를 유지하면, 시스템의 장애나 문제가 발생했을 때도 빠르게 대응하고 복구할 수 있다.
- DB 부하 분산 : 읽기(Read) 작업과 쓰기(Write) 작업을 분할함으로써 DB 부하를 분산시켜 빠른 성능으로 응답할 수 있다. 읽기, 쓰기, 수정의 모든 연산이 하나의 DB에서 일어난다면 트래픽이 늘어남에 따라 자연스럽게 병목 현상이 생길 수 있기 때문이다.
원리
MySQL Replication 설정을 통해서, 다른 서버에 존재하는 2개의 MySQL을 연결한다.
Master 서버는 쓰기만 가능, Slave 서버는 읽기만 가능하게끔 설정하면 데이터베이스 분산을 할 수 있다.
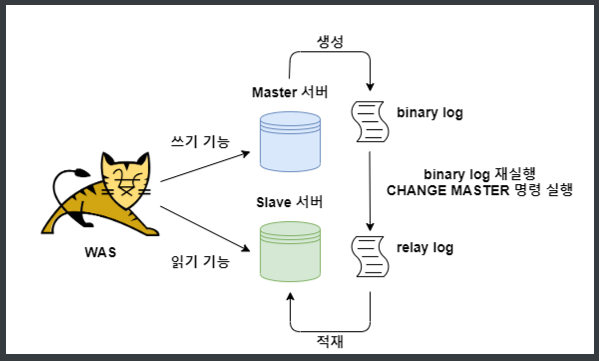
- 클라이언트가 Commit 을 누르면 먼저 Master 서버에 존재하는 Binary log 에 변경사항을 모두 기록한다.
- Master Thread 는 비동기적 으로 Binary log를 읽어 Slave 서버로 전송한다.
- Slave 의 I/O Thread 는 Master로 부터 받은 변경 데이터들을 Relay log 에 기록한다.
- Slave의 SQL Thread 는 Relay log의 기록들을 읽어 자신의 스토리지 엔진에 최종 적용한다.
구현하기
@Transactional(readOnly = true) 가 붙어있는 메서드의 경우 Slave 서버로 읽기 작업을 하도록 설정하고
@Transactional 이 붙어있는 메서드의 경우 Master 서버로 쓰기 작업을 하도록 설정할 것이다.
Application.yml 설정
spring:
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
datasource:
master:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc-url : jdbc:mysql://'master 서버 IP':3306/'db명'
username : root
password :
slave:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://'slave 서버 IP':3306/'db명'
username: root
password:
master로 사용할 서버와 slave로 사용할 서버가 다르기 떄문에
application.yml의 datasource 설정을 추가해주어야 한다.
MySQL Replication 구축 과정은 여기서 참고하면 된다.
DynamicRoutingDataSource 클래스
Transaction이 readOnly인지 판단하는 클래스이다.
public class DynamicRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return isCurrentTransactionReadOnly() ? SLAVE : MASTER;
}
}
AbstractRoutingDataSource 클래스는 DataSource의 구현 클래스이고,
이를 상속받아 현제 사용중인 데이터 소스 식별자를 반환하는 determineCurrentLookupKey() 메서드를 오버라이딩한다.
isCurrentTransactionReadOnly() 메서드는 메서드 명으로 알 수 있듯이, 현재 트랜잭션이 readOnly 인지 아닌지 반환한다.
public class DataSourceConstants {
public static final String MASTER = "master";
public static final String SLAVE = "slave";
}
참고로, 식별자는 위와 같이 enum 타입으로 관리했다.
DataSourceConfig 클래스
DynamicRoutingDataSource 에서 반환하는 식별자에 따라,
JPA가 특정 데이터 소스를 사용할 수 있도록 해야하기 때문에 구현해야하는 클래스이다.
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class DataSourceConfig {
private final Environment env;
@Bean(name = "masterDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.master")
public DataSource masterDataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "slaveDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.slave")
public DataSource slaveDataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@DependsOn({"masterDataSource", "slaveDataSource"})
@Bean
public DataSource routingDataSource(
@Qualifier("masterDataSource") DataSource master,
@Qualifier("slaveDataSource") DataSource slave) {
DynamicRoutingDataSource routingDataSource = new DynamicRoutingDataSource();
Map<Object, Object> dataSourceMap = new HashMap<>();
dataSourceMap.put(MASTER, master);
dataSourceMap.put(SLAVE, slave);
routingDataSource.setTargetDataSources(dataSourceMap);
routingDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(master);
return routingDataSource;
}
@DependsOn({"routingDataSource"})
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(DataSource routingDataSource) {
return new LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy(routingDataSource);
}
@Bean
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory(DataSource dataSource) {
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean em = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
em.setJpaVendorAdapter(new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter());
em.setDataSource(dataSource);
em.setPackagesToScan("com.shoekream.domain");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto", env.getProperty("spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto"));
properties.setProperty("hibernate.show_sql", "true");
em.setJpaProperties(properties);
return em;
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory) {
JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setEntityManagerFactory(entityManagerFactory);
return transactionManager;
}
}
먼저 전체 코드는 위와 같다.
어노테이션 정리
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class DataSourceConfig {
...//
먼저, 이 클래스는 여러개의 빈을 갖기 때문에 @Configuration 어노테이션을 붙인다.
JPA를 자동 구성으로 사용할 때는, DataSourceAutoConfiguration 클래스가
DataSource , EntityManagerFactory 빈을 자동으로 구성하게 된다.
하지만, 우리는 커스터마이징한 DataSource를 적절할 때에 사용하도록 해야하므로
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class}) 를 추가함으로서 자동 구성된 빈 때문에 빈 충돌이 발생하는 것을 방지한다.
PlatformTransactionManager 정의
@EnableTransactionManagement 어노테이션은 트랜잭션 관리를 위해 필요한 여러 구성 요소를 자동으로 구성해주기 때문에 필요하다.
그 중에서 PlatformTransactionManager 빈도 자동으로 생성해주지만, 직접 정의한 EntityManagerFactory 를 주입해주어야 하므로 아래와 같은 설정을 추가해준다.
@Primary
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory) {
JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setEntityManagerFactory(entityManagerFactory);
return transactionManager;
}
@EnableTransactionManagement이 자동으로 생성하는 빈과, 빈 충돌이 발생하지 않도록 @Primary 어노테이션을 붙여준다.
DataSource Master용 Bean, Slave용 Bean 정의
@Bean(name = "masterDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.master")
public DataSource masterDataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "slaveDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.slave")
public DataSource slaveDataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
application.yml 에서 입력한 master와 slave 관련 설정들이 주입된 DataSource 빈을 생성하는 구문이다.
이렇게 만든 2개의 DataSource 빈을, 적절한 때에 적절한 것을 사용하게끔 하는 것이다.
@DependsOn({"masterDataSource", "slaveDataSource"})
@Bean
public DataSource routingDataSource(
@Qualifier("masterDataSource") DataSource master,
@Qualifier("slaveDataSource") DataSource slave) {
DynamicRoutingDataSource routingDataSource = new DynamicRoutingDataSource();
Map<Object, Object> dataSourceMap = new HashMap<>();
dataSourceMap.put(MASTER, master);
dataSourceMap.put(SLAVE, slave);
routingDataSource.setTargetDataSources(dataSourceMap);
routingDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(master);
return routingDataSource;
}
@DependsOn 어노테이션을 통해, masterDataSource 와 slaveDataSource 빈이 모두 생성된 후에 생성되도록 지정한다.
그리고, 파라미터로는 DataSource 빈이 2개 있으므로, @Qaulifier 어노테이션으로 주입받을 빈을 명시해준다.
그리고, 이전에 return isCurrentTransactionReadOnly() ? SLAVE : MASTER; 식별자를 이렇게 반환하도록 설정했으므로
식별자에 따라, 사용되는 DataSource가 달라질 것이다.
LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy 정의
@DependsOn({"routingDataSource"})
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(DataSource routingDataSource) {
return new LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy(routingDataSource);
}
위에서 생성된 routingDataSource 빈이 생성되고 나서 생성되는 빈이다.
LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy 을 사용하면, 프록시 객체를 통해 실제 데이터 소스를 지연 초기화하여, 애플리케이션 시작 시점에 모든 데이터 소스를 미리 초기화하는 것을 방지할 수 있다.
이중화 하기 전에는, 어차피 사용할 데이터 소스가 하나여서 동적으로 지정할 필요가 크게 없었지만,
지금은 2개의 데이터 소스를 갖고 있으므로 데이터 소스를 동적으로 지정해야한다.
이를 통해, 애플리케이션 시작 시점에 모든 데이터 소스를 초기화하는 것이 아니라, 필요한 데이터 소스가 요청되는 시점에 초기화될 수 있도록 구현할 수 있다.
entityManagerFactory 정의
@Bean
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory(DataSource dataSource) {
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean em = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
em.setJpaVendorAdapter(new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter());
em.setDataSource(dataSource);
em.setPackagesToScan("com.shoekream.domain");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto", env.getProperty("spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto"));
em.setJpaProperties(properties);
return em;
}
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class}) 를 추가했기 때문에, entityManagerFactory 빈도 직접 설정해주어야한다.
DataSource를 주입해주고, 엔티티가 존재하는 패키지를 명시해준다.
그리고, 그 외 필요한 설정들을 넣어주면 되는데,
application.yml의 ddl-auto 설정을 넣어주었다.
참고 : https://tecoble.techcourse.co.kr/post/2021-10-14-springboot-autoconfiguration/